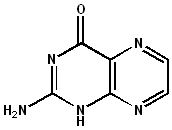
Pterin
Pterin is a heterocyclic compound that forms the core structure of a variety of biologically significant molecules known as pteridines. Pterins are involved in numerous biological processes, including the metabolism of folic acid and the synthesis of neurotransmitters.
Structure and Properties[edit | edit source]
Pterin consists of a pyrimidine ring fused to a pyrazine ring. The chemical formula for pterin is C6H5N5O. The structure of pterin allows it to participate in various biochemical reactions, particularly those involving redox processes.
Biological Significance[edit | edit source]
Pterins play a crucial role in the function of several enzymes. One of the most well-known pterins is tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which acts as a cofactor for the hydroxylation of aromatic amino acids such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. This process is essential for the synthesis of important neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
Metabolism[edit | edit source]
The metabolism of pterins involves several key enzymes, including dihydropteridine reductase and sepiapterin reductase. These enzymes are responsible for the regeneration and recycling of tetrahydrobiopterin, ensuring its availability for various metabolic processes.
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
Deficiencies in pterin metabolism can lead to a range of medical conditions. For example, a deficiency in tetrahydrobiopterin can result in hyperphenylalaninemia, which is associated with phenylketonuria (PKU). Additionally, abnormalities in pterin metabolism have been linked to various neurological disorders.
Research and Applications[edit | edit source]
Research into pterins has expanded our understanding of their role in human health and disease. Pterins are also being studied for their potential therapeutic applications, including their use as biomarkers for certain diseases and their role in the development of new drugs.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Translate: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Navigation: Wellness - Encyclopedia - Health topics - Disease Index - Drugs - World Directory - Gray's Anatomy - Keto diet - Recipes
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD