Dissolved air flotation
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewater (or other types of water) by the removal of suspended matter such as oils, greases, or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank or basin. The released air forms tiny bubbles that adhere to the suspended matter, causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.
Process[edit | edit source]
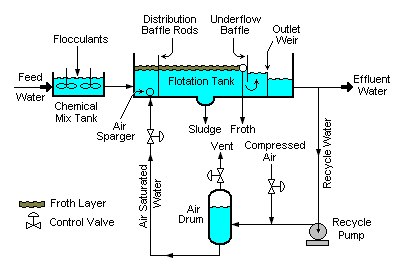
The DAF process consists of several key components: air supply, pressurizing pump, air saturation tank, flotation tank, and skimmer. The process begins with the water to be treated entering the DAF flotation tank. A stream of water is then taken from the tank and pressurized. Air is introduced into this pressurized stream, usually by means of a venturi nozzle, which causes the air to dissolve into the water due to the high pressure. This air-saturated water stream is then released back into the flotation tank at atmospheric pressure. As the pressure is released, the dissolved air comes out of solution in the form of microbubbles.
These microbubbles attach to the particles of suspended matter, reducing their density and causing them to rise to the surface of the water. At the surface, a floating layer of material, referred to as a "float", forms. This float is then removed from the surface by a skimming mechanism. The clarified water is collected from the bottom of the tank.
Applications[edit | edit source]
DAF is widely used in the treatment of industrial wastewater, such as that from chemical plants, oil refineries, and paper mills, to remove oils and other suspended solids. It is also used in the pretreatment of drinking water, where it helps to reduce the load on downstream filtration processes. In addition, DAF is employed in some types of aquaculture, to remove fine particles such as algae from recirculating water systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
The main advantage of DAF is its ability to treat high flows of water and efficiently remove a wide range of suspended materials. It is particularly effective for particles that are too small to settle by gravity in a reasonable time or that have a density close to that of water.
However, DAF systems can be expensive to operate due to the energy required to pressurize the water and air. They also require careful control of operating conditions to ensure efficient removal of suspended matter. Maintenance of the system and its components, particularly the air saturation system and the skimming mechanism, is critical for effective operation.
Environmental Impact[edit | edit source]
DAF systems can have a positive impact on the environment by improving the quality of industrial and municipal wastewater discharges. However, the process must be carefully managed to ensure that it does not lead to the release of concentrated waste materials into the environment. Proper disposal or further treatment of the removed solids is necessary to minimize environmental impact.
Navigation: Wellness - Encyclopedia - Health topics - Disease Index - Drugs - World Directory - Gray's Anatomy - Keto diet - Recipes
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD